分散スイッチで Netflow を有効化する
Netflow は Cisco 社が開発した、ネットワークのトラフィックを収集・分析するための技術です。VMware 社の分散スイッチでは、NetFlow をサポートしており、ポートグループに流れるトラフィックを、コレクターに出力する事が可能です。
分散スイッチの設定
対象の分散スイッチを右クリックし「Manage Distributed Port Groups」をクリックします。

「Monitoring」を選択し「Next」をクリックします。

対象のポートグループを選択し「Next」をクリックします。

Netflow を「Enabled」に設定し「Next」をクリックします。

内容を確認し「Finish」をクリックします。

分散スイッチを選択し「Manage」タブの NetFlow で、コレクターの設定等を行います。

Netflow コレクタ(PRTG)の設定
「Sensors」タブから「Add Sensor」をクリックします。

「Create a new Device」を選択し「Continue」をクリックします。

Group を選択し「Continue」をクリックします。

「Device Name」「IP Address」を設定し「Continue」をクリックします。

「UDP port」「Active Flow Timeout」を設定し「Continue」をクリックします。

ポートグループ間のトラフィック状況をモニターする事が可能となります。

VMware PowerCLI サンプルスクリプト
CSV ファイルを読み込んで、仮想マシンを制御するスクリプトの例です。
本例では、仮想マシン名を記述した CSV ファイル(vms.csv)を以下のパスに配置しています。
C:\scripts\vms.csv
CSV ファイルの内容は、以下のとおりです。

仮想マシンを起動するスクリプト
$vCenterIP = "192.168.1.10" $User = "Administrator" $Password = "Password" $VMs = Import-CSV C:\scripts\vms.csv #Import the PowerCLI module Add-PSSnapin VMware.VimAutomation.Core #Connect to the server $vi = Connect-VIServer -Server $vCenterIP -User $User -Password $Password #Power on the VMs foreach ($vm in $VMs){ Get-VM $vm.VMName | where{$_.PowerState -eq "PoweredOff"} | Start-VM -Runasync -Confirm:$false | Out-Null } #Disconnect to the server Disconnect-VIServer -Server $vCenterIP -Confirm:$False
仮想マシンを停止するスクリプト
$vCenterIP = "192.168.1.10" $User = "Administrator" $Password = "Password" $VMs = Import-CSV C:\scripts\vms.csv #Import the PowerCLI module Add-PSSnapin VMware.VimAutomation.Core #Connect to the server $vi = Connect-VIServer -Server $vCenterIP -User $User -Password $Password #Power off the VMs foreach ($vm in $VMs){ Get-VM $vm.VMName | where{$_.PowerState -eq "PoweredOn"} | Shutdown-VMguest -Confirm:$false | Out-Null } #Disconnect to the server Disconnect-VIServer -Server $vCenterIP -Confirm:$False
仮想マシンのスナップショットを取得するスクリプト
$vCenterIP = "192.168.1.10" $User = "Administrator" $Password = "Password" $Date = Get-Date -format yyyyMMddHHmm $VMs = Import-CSV C:\scripts\vms.csv #Import the PowerCLI module Add-PSSnapin VMware.VimAutomation.Core #Connect to the server $vi = Connect-VIServer -Server $vCenterIP -User $User - #Create the Snapshot foreach ($vm in $VMs){ New-Snapshot -Name $Date -VM $vm.VMName -Descript } #Disconnect to the server Disconnect-VIServer -Server $vCenterIP -Confirm:$False
仮想マシンのスナップショットを削除するスクリプト
$vCenterIP = "192.168.1.10" $User = "Administrator" $Password = "Password" $Date = Get-Date -format yyyyMMddHHmm $VMs = Import-CSV C:\scripts\vms.csv #Import the PowerCLI module Add-PSSnapin VMware.VimAutomation.Core #Connect to the server $vi = Connect-VIServer -Server $vCenterIP -User $User -Password $Password #Remove the Snapshot foreach ($vm in $VMs){ Get-Snapshot -VM $vm.VMName | Remove-Snapshot -RemoveChildren -Confirm:$False } #Disconnect to the server Disconnect-VIServer -Server $vCenterIP -Confirm:$False
参考書籍
以上
VMware Workstation で vFRC を試す
vFRC とは
仮想ディスクの Read Cache として、ローカルサーバの SSD を利用する仕組みを提供します。この機能により、仮想ディスクの読み込み速度が向上し、ストレージの負荷を軽減することが可能です。
詳細については、こちらをご参照ください。
事前準備
VMware Workstation では、SSD デバイスをシミュレートすることが可能です。対応する仮想マシンの vmx ファイルを編集し、SSD をシミュレートしたい SCSI デバイスを対象に下記を追記します。
scsiX:Y.virtualSSD = 1
対象の SCSI デバイスが SSD として、認識されます。
ESXi 側の vFRC の設定
Manage > Settings > Virtual Flash Resource Management > Add Capacity をクリックします。

有効な SSD デバイスが表示されるので、選択し「OK」をクリックします。

Device Backing のリストに SSD デバイスが追加されます。

ESXi ホストの vmkernel swap 領域として使用する場合は、下記の手順で行います。
Manage > Settings > Virtual Flash Host Swap Cache Configuration > Edit をクリックします。

キャッシュ容量を指定し「OK」をクリックします。

ホストキャッシュが設定されていることを確認します。

仮想マシン側の vFRC の設定
対象の仮想マシンの編集から、仮想ディスクを展開し vFRC の「Advanced」をクリックします。

キャッシュ容量とブロックサイズを指定し「OK」をクリックします。

「OK」をクリックします。

なお、この手順は、仮想マシンがパワーオン状態でも実施可能です。
vSphere Replication について
任意の仮想マシンについて、ハイパーバイザレベルでレプリケーションを実施する機能になります。
仮想マシンのコピーをハイパーバイザレベルで実施するため、データストアに依存しない点が特徴になります。

初期設定
vSphere Replication をインストール後、必要に応じて基本設定を行います。
仮想アプライアンスへの下記のアドレス・ポートでアクセス可能です。
https://IP_of_your_VR_appliance:5480

仮想アプライアンスを起動後、vCenter に VR のアイコンが追加されます。

Replication の構成例
対象の仮想マシンを選択し、右クリックから「Configure Replication」をクリックします。

vSphere Replication Server を選択し「Next」をクリックします。

Replication 先のデータストアを選択し「Next」をクリックします。

HDD をコピーする場合は「Enable disk replication」を選択し「Next」をクリックします。

「Next」をクリックします。

RPO(Recovery Point Objective)を設定し「Next」をクリックします。*3

内容を確認し「Finish」をクリックします。

Monitor > vSphere Replication > Outgoing Replication から、状態を確認できます。

仮想マシンのリカバリ
対象の仮想マシンを選択し、右クリックから「Recover」をクリックします。

Recovery options を選択し「Next」をクリックします。

仮想マシンの配置先 Folder を選択し「Next」をクリックします。

仮想マシンの配置先 Cluster を選択し「Next」をクリックします。

内容を確認し「Finish」をクリックします。

分散スイッチの作成とマイグレート
vSphere Web Client を使用した分散スイッチの作成と、標準スイッチからの移行を試してみました。
分散スイッチの作成
「Networking」タブで「Datacenter」を右クリックし「New Distributed Switch」をクリックします。

「Name」を設定し「Next」をクリックします。

「Version」を指定し「Next」をクリックします。

「Port group name」等を設定し「Next」をクリックします。

内容を確認し「Finish」をクリックします。

分散スイッチへのホスト登録
「Networking」タブで「DSwitch」を右クリックし「Add and Manage Hosts」をクリックします。

「Add hosts」を指定し「Next」をクリックします。

「New hosts」をクリックします。

「Host」を選択し「OK」をクリックします。

内容を確認し「Next」をクリックします。

「Next」をクリックします。

分散スイッチに追加する仮想 NIC を選択し「Assign uplink」をクリックします。

仮想 NIC を紐づける Uplink を選択し「OK」をクリックします。

内容を確認し「Next」をクリックします。

既存の vmkernel は移行対象外なので「Next」をクリックします。

「Next」をクリックします。

内容を確認し「Finish」をクリックします。

分散スイッチにホストが追加されている事を確認します。

標準スイッチから分散スイッチへの移行
「Networking」タブで「DSwitch」を右クリックし「Migrate VM to Another Network」をクリックします。

Source Network の「Specific Network」で「Browse」をクリックします。

移行元(標準スイッチ)のポートグループを選択して「OK」をクリックします。

Destination Network の「Specific Network」で「Browse」をクリックします。

移行先(分散スイッチ)のポートグループを選択して「OK」をクリックします。

内容を確認し「Next」をクリックします。

移行対象の仮想マシンを選択して「Next」をクリックします。

内容を確認し「Finish」をクリックします。

対象の仮想マシンが分散スイッチに移行している事を確認します。

busy,LUNs 状態の Snapshot について
SnapManager for Exchange (SME) 等のベリファイ処理失敗時に、残存する Snapshot になります。
以下の手順で削除する事が可能です。
snap list コマンドで busy 状態の Snapshot を確認します。
> snap list testvol Volume testvol working... %/used %/total date name ---------- ---------- ------------ -------- <...snip...> 56% (12%) 26% ( 3%) Dec 18 05:01 exchsnap__exchange_02-23-2009_05.00.40 (busy,LUNs)
Snapmirror の送信元/送信先で Clone LUN が存在する事を確認します。
> lun show <...snip...> /vol/testvol/{3fd1acat-346c-216d-b6e4-bdf90a52801f}.rws
Snapmirror 送信先で snapmirror break を実行します。
> snapmirror break testvol
Snapmirror 送信先で lun offline/lun destroy を実行します。
> lun offline /vol/testvol/{3fd1acat-346c-216d-b6e4-bdf90a52801f}.rws > lun destroy /vol/testvol/{3fd1acat-346c-216d-b6e4-bdf90a52801f}.rws
SnapDrive にて、Clone LUN をマウントしている場合は、Disconnect Disk を実行します。
Snapmirror 送信元で不要な Snapshot を削除します。
> snap delete testvol exchsnap__exchange_02-23-2009_05.00.40
Snapmirror resync を実行します。
> snapmirror resync -S [Sorce]:testvol testvol
以上
sdw_cl_vol について
sdw_cl_vol について
SnapManager for Exchange (SME) 等のベリファイ時に、ミラー先で生成されるボリュームです。
ベリファイ成功時は自動で削除されますが、失敗時は残留する場合があります。
これが残留していると、対象の Snapshot が busy 状態となり、次回のベリファイも失敗する可能性があります。
ボリューム名は、sdw_cl_[volname]_0 で生成されます。
> df -h Filesystem total used avail capacity Mounted on /vol/sdw_cl_testvol_0/ 100GB 50GB 50GB 50% /vol/sdw_cl_testvol_0/ /vol/sdw_cl_testvol_0/.snapshot 0KB 1000KB 0KB ---% /vol/sdw_cl_testvol_0/.snapshot
対象ボリュームの Snapshot 状況を確認すると、busy 状態の Snapshot が存在します。
> snap list testvol Volume testvol working... %/used %/total date name ---------- ---------- ------------ -------- 0% ( 0%) 0% ( 0%) Jan 16 06:12 netapp(0151729559)_testvol.1747 0% ( 0%) 0% ( 0%) Jan 16 06:12 @snapmir@{93F9293E-17BB-4AF5-91D6-FBEFBDCFCCFE} 0% ( 0%) 0% ( 0%) Jan 16 06:01 exchsnap__exchange_01-01-2015_06.00.46 (busy,snapmirror,vclone)
以下のコマンドで、sdw_cl_vol を削除します。
> vol offline sdw_cl_testvol_0 > vol destroy sdw_cl_testvol_0
対象ボリュームの Snapshot 状況を確認すると、busy 状態の Snapshot が削除されています。
> snap list testvol Volume testvol working... %/used %/total date name ---------- ---------- ------------ -------- 0% ( 0%) 0% ( 0%) Jan 16 06:12 netapp(0151729559)_testvol.1747 0% ( 0%) 0% ( 0%) Jan 16 06:12 @snapmir@{93F9293E-17BB-4AF5-91D6-FBEFBDCFCCFE}
以上
vSphere Web Client でゲストへ接続できない問題について
vSphere Web Client で仮想マシンのコンソールを開く際、下記のように「サーバ名を解決できませんでした」というエラーが表示される場合があります。

考えられる原因の1つとして、クライアントから vCenter 及び、ESXi サーバの名前解決ができていない可能性があります。この場合、DNS を使用するか、下記のように hosts に登録する事で収束します。
# Copyright (c) 1993-2009 Microsoft Corp. # # This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows. # # This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each # entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should # be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name. # The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one # space. # # Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual # lines or following the machine name denoted by a '#' symbol. # # For example: # # 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server # 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host # localhost name resolution is handled within DNS itself. # 127.0.0.1 localhost # ::1 localhost 192.168.1.10 vcenter55.example.com 192.168.1.11 esxi01.example.com 192.168.1.12 esxi02.example.com
Wireshark のフィルタリング
良く使うフィルタリング設定のメモ
送信元 IP アドレスが「192.168.1.1」のパケットのみを表示
ip.src == 192.168.1.1
送信先 IP アドレスが「192.168.2.1」のパケットのみを表示
ip.dst == 192.168.1.1
送信元 IP アドレスが「192.168.1.1」かつ、ポートが「80」のパケットのみを表示
ip.src == 192.168.1.1 and tcp.port == 80
TCP の SYN フラグが設定されたパケットを表示
tcp.flags.syn==1
TCP の ACK フラグが設定されたパケットを表示
tcp.flags.ack==1
TCP の SYN か ACK フラグが設定されたパケットを表示
tcp.flags.syn==1 or tcp.flags.ack==1
HTTP のステータスコードが400以上のパケットを表示
http.response.code >= 400
vSphere Management Assistant(vMA)について
vMAとは
vSphere Command Line Interface(vCLI)等のコンポーネントを含む無償の仮想アプライアンスです。
こちらからダウンロード可能です。
vMA の使い方(例)
ドメインへの参加
> sudo domainjoin-cli join example.com Administrator
vMA ドメイン参加状況確認
> sudo domainjoin-cli query
VMA をドメインから削除
> sudo domainjoin-cli leave
ファストパスの設定
> vifp addserver esxi01.example.com --authpolicy fpauth --username root
ファストパスの確認
> vifp listservers
ターゲットへのアクセス
> vifptarget -s esxi01.example.com
ホストの日時を確認
[esxi01.example.com]> esxcli hardware clock get 2014-12-22T11:23:29Z
ホストの CPU を確認
[esxi01.example.com]> esxcli hardware cpu list CPU:0 Id: 0 Package Id: 0 <...snip...>
ホストのメモリを確認
[esxi01.example.com]> esxcli hardware memory get Physical Memory: 4294430720 Bytes Reliable Memory: 0 Bytes NUMA Node Count: 1
ホスト上の仮想マシンを確認
[esxi01.example.com]> vmware-cmd -l /vmfs/volumes/36b7b309-58b356ee/vMA/vMA.vmx /vmfs/volumes/36b7b309-58b356ee/MyVM2_1/MyVM2.vmx /vmfs/volumes/36b7b309-58b356ee/MyVM1/MyVM1.vmx
仮想マシンのスナップショット確認
[esxi01.example.com]> vmware-cmd /vmfs/volumes/36b7b309-58b356ee/vMA/vMA.vmx hassnapshot hassnapshot () = 0
resxtop の実行
[esxi01.example.com]> resxtop
11:30:43am up 1 day 4:39, 433 worlds, 3 VMs, 3 vCPUs; CPU load average: 0.59, 0.57, 0.60
PCPU USED(%): 0.0 0.0 AVG: 0.0
PCPU UTIL(%): 0.0 0.0 AVG: 0.0
ID GID NAME NWLD %USED %RUN %SYS %WAIT %VMWAIT %RDY %IDLE %OVRLP %CSTP %MLMTD %SWPWT
1 1 idle 2 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 - 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
2 2 system 63 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 - 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
8 8 helper 134 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 - 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
9 9 drivers 14 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 - 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
10 10 ft 5 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 - 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
11 11 vmotion 1 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 - 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
8612 8612 MyVM2 7 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
8660 8660 MyVM1 7 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
531100 531100 vMA 7 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
スナップショットを削除するスクリプト
セキュリティポリシーの変更(スクリプトの実行を許可)
PS C:\> Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
対象の仮想マシンのスナップショットを削除するスクリプト例になります。
※-RemoveChildren は「すべて削除」と同義です。指定しない場合は、1つずつ削除します。
$vCenterIP = "192.168.1.10" $User = "Administrator" $Password = "Password" $VM = "POCVM001" #Import the PowerCLI module Add-PSSnapin VMware.VimAutomation.Core #Connect to the server $vi = Connect-VIServer -Server $vCenterIP -User $User -Password $Password #Remove the Snapshot Get-Snapshot -VM $VM | Remove-Snapshot -RemoveChildren -Confirm:$False #Disconnect to the server Disconnect-VIServer -Server $vi -Confirm:$False
タスクスケジューラを使用する場合は、プログラム/スクリプトと引数を下記のとおり指定します。
C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
-psc "C:\Program Files (x86)\VMware\Infrastructure\vSphere PowerCLI\vim.psc1" -file "C:\Scripts\test.ps1"
参考書籍
以上
セカンダリアドレスで HSRP
セカンダリアドレスで HSRP が可能か試してみました。環境は下記のとおりです。
ルータは、CSR1000V IOS XE Version: 03.09.02.S を使用しました。
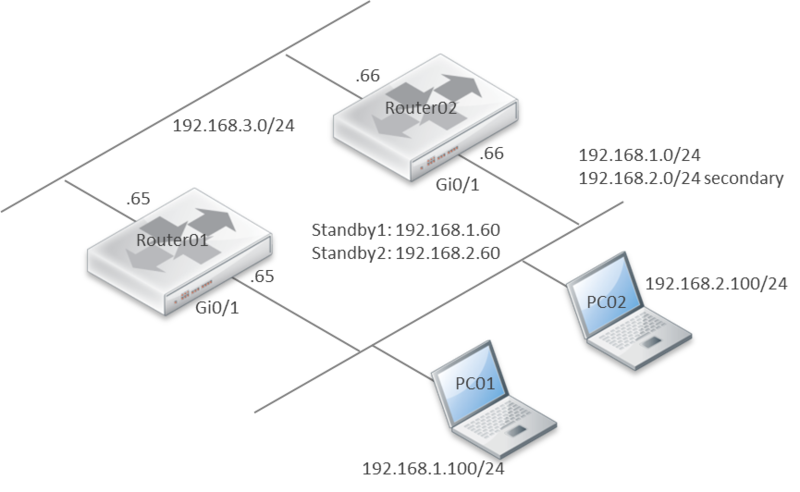
結論から言えば、上記の環境では、セカンダリアドレスで HSRP は可能でした。
アドレス不足により、同一のブロードキャストドメインに、複数の異なるサブネットを共存させたい際等に活用できそうです。ただし、運用管理上の観点から、多用は避けた方が良いかもしれません。
Router01 はプライマリアドレスを Active、セカンダリアドレスを Standby として認識。
Router01#show standby brief
P indicates configured to preempt.
|
Interface Grp Pri P State Active Standby Virtual IP
Gi1 1 110 P Active local 192.168.1.66 192.168.1.60
Gi1 2 90 P Standby 192.168.2.66 local 192.168.2.60Router02 はプライマリアドレスを Standby、セカンダリアドレスを Active として認識。
Router02#show standby brief
P indicates configured to preempt.
|
Interface Grp Pri P State Active Standby Virtual IP
Gi1 1 90 P Standby 192.168.1.65 local 192.168.1.60
Gi1 2 110 P Active local 192.168.2.65 192.168.2.Router01 設定例
Router01#show running-config interface gigabitEthernet 1 interface GigabitEthernet1 ip address 192.168.2.65 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 192.168.1.65 255.255.255.0 standby 1 ip 192.168.1.60 standby 1 priority 110 standby 1 preempt standby 2 ip 192.168.2.60 standby 2 priority 90 standby 2 preempt
Router02 設定例
Router02#show running-config interface gigabitEthernet 1 interface GigabitEthernet1 ip address 192.168.2.66 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 192.168.1.66 255.255.255.0 standby 1 ip 192.168.1.60 standby 1 priority 90 standby 1 preempt standby 2 ip 192.168.2.60 standby 2 priority 110 standby 2 preempt
以上
VMware スナップショットの注意点
VMware のスナップショットとは
スナップショットには、スナップショット作成時の仮想マシンの状態とデータが保存されます。仮想マシンのスナップショットを作成すると、特定の状態の仮想マシンのイメージがコピーおよび保存されます。スナップショットは、繰り返し同じ状態の仮想マシンに戻る必要があるが、複数の仮想マシンを作成したくないという場合に便利です。
…(中略)…
出典:VMware, Inc
スナップショットに含まれる情報
- 仮想マシンの設定:ディスクを含む、仮想マシン ディレクトリ
- 電源状態:パワーオン状態、パワーオフ状態、またはサスペンド状態
- ディスク状態:仮想ディスクの状態。
- メモリ状態(任意):仮想マシンのメモリの内容
VMware スナップショットの注意点
スナップショットを削除した際、仮想マシンが数分間停止する事象があったので、メモ。
参考:A snapshot removal can stop a virtual machine for long time (1002836)
スナップショット作成時の動作
スナップショットを作成すると、delta.vmdk が作成されます。
例えば、1つの仮想マシンとスナップショットのファイル構成は、下記のとおりです。
- disk.vmdk with extent disk-flat.vmdk
- disk-000001.vmdk with extent disk-000001-delta.vmdk
スナップショット作成後、この delta.vmdk で差分情報を収容していきます。
スナップショット削除時の動作
スナップショットを削除、または結合した場合、Consolidate Helper Snapshot と呼ばれるスナップショットが、ディスク I/O に比例して複数作成されます。
- disk.vmdk with extent disk-flat.vmdk
- disk-000001.vmdk with extent disk-000001-delta.vmdk
- disk-000002.vmdk with extent disk-000002-delta.vmdk
delta.vmdk と親ディスクである flat.vmdk は整合性保全のため、Read-only となり、データは、この Consolidate Helper Snapshot へ書き込まれます。しかし、最終的には、この Consolidate Helper Snapshot も flat.vmdk へマージしなければいけないため、この間仮想マシンが停止します。この事から、スナップショットを削除する際は、十分に注意して、ディスク I/O が極力少ない状況下で、実施する事を推奨します。
また、VMware 社は、スナップショットの保持について、72時間(3日)以上、保持しない事を推奨しています。
Best practices for virtual machine snapshots in the VMware environment (1025279)
Use no single snapshot for more than 24-72 hours.
スナップショットによる副作用
データストアに、NetApp ストレージを利用している場合は、次の点にも注意が必要です。
仮想マシンのスナップショットは、512Byte で差分を管理しているため、Partial Write が発生します。
Partial Write とは、4KBbyte 以下のデータに対して書き込みが発生した際(NetApp の仕様上)直接書き込みする事はできないため、対象のブロックを一度読み出し、部分的更新を行ってから、ディスク書き込む処理の事です。このため、スナップショットが存在している場合、無駄な Read が発生していると考えられます。
以上
Multi-VRF 環境での OSPF について
Multi-VRF 環境での OSPF について、標準エリア上で受信した LSA Type-3 の情報を(データベース上には存在するが)ルーティングテーブル上に反映できない事象を確認しました。通常、DN Bit が付与された LSA を受信した場合は、ルーティングループを防止するため、このような事象が発生します。
しかし、今回検証した環境では、MP-BGP を使用しておらず、DN Bit は付与されていません。

DN Bit が付与された場合は、Options: の一番右が Downward となります。
R1#show ip ospf database summary
OSPF Router with ID (192.168.1.101) (Process ID 1)
Summary Net Link States (Area 1)
LS age: 751
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC, Upward)
LS Type: Summary Links(Network)
Link State ID: 10.2.2.1 (summary Network Number)
Advertising Router: 192.168.1.102
LS Seq Number: 8000000C
Checksum: 0x4908
Length: 28
Network Mask: /32
MTID: 0 Metric: 1LSA Type-1 及び Type-5 はルーティングテーブルに反映できています。
R1#show ip route vrf poc ospf | begin Gateway
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 10.2.2.2 [110/2] via 192.168.1.102, 00:08:33, GigabitEthernet2
172.16.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O E2 172.16.2.1 [110/1] via 192.168.1.102, 00:08:33, GigabitEthernet2OSPF プロセスで capability vrf-lite*1を有効にすると、Type-3 の情報も反映します。
R1(config-router)#router ospf 1 vrf poc
R1(config-router)#capability vrf-lite
R1(config-router)#end
R1#show ip route vrf poc ospf | begin Gateway
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 2 subnets
O IA 10.2.2.1 [110/2] via 192.168.1.102, 00:04:37, GigabitEthernet2
O 10.2.2.2 [110/2] via 192.168.1.102, 00:04:37, GigabitEthernet2
172.16.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O E2 172.16.2.1 [110/1] via 192.168.1.102, 00:04:37, GigabitEthernet2OSPF Command Reference における capability vrf-lite の説明は以下のとおりです。
The table below describes the PE checks performed when Type-3, Type-5, and Type-7 LSAs are received.
| Type-3 LSA received | The DN bit is checked. If the DN bit is set, the Type-3 LSA is not considered during the shortest path first (SPF) calculation. |
| Type-5 or -7 LSA received | If the Tag in the LSA is equal to the VPN-tag, the Type-5 or-7 LSA is not considered during the SPF calculation. |
With the capabilityvrf-lite command, the checks can be turned off to allow correct population of the VRF routing table with routes to IP prefixes.
この説明からは、DN Bit が付与されていない LSA Type-3 は SPF 計算の対象となると読み取れます。
DN Bit が付与されていない LSA Type-3 の情報を、ルーティングテーブルに反映できない事象は、仕様なのか、不具合なのか、引き続き調査を進めたいと思います。
※2014/9/1 追記
上記動作については、ソフトウェアの仕様である事が判明しました。
なお、ドキュメント上で明確になっていない事から「ドキュメントのバグ」として、修正依頼をかけて頂く事になりました。
以上
*1:このコマンドを実行すると、有効な Neighbor がダウンするため、注意が必要です
コマンドを任意の時間に実行するスクリプト
基本的な考え方として、ビジーウェイトによる非効率性に対処するため、スクリプト実行時間(TARGET_TIME)まで、sleep するようになっています。下記は、12:00 に SnapMirror の状態を確認する場合の例になります。
#!/usr/bin/perl use Time::Local; use POSIX 'strftime'; use IO::Handle; $TARGET_TIME = "12:00"; #------------------------------ if ( $#ARGV != 0) { print "usage : perl test.pl [SystemName]\n"; exit; } $sHostname = $ARGV[0]; shift( @ARGV ); while(1) { $nTime = strftime( "%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S" , localtime ); $nTime2 = strftime( "%H:%M:%S %Y/%m/%d" , localtime ); $nSec = strftime( "%S" , localtime ); $nTime3 = strftime( "%H:%M" , localtime ); $nDate = strftime( "%Y%m%d_%H%M%S" , localtime ); print "$nTime : target = $sHostname\n"; if ($nTime3 eq $TARGET_TIME) { $str = "sshpass -p PASSWORD ssh -l root $sHostname snapmirror status > /tmp/${nDate}_$sHostname.log"; print "command : $str\n"; system( $str ); last; } $n = 60 - $nSec; sleep( $n ); } #------------------------------